8 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit: A Simple Guide To Temperature Conversion
Have you ever found yourself scratching your head trying to figure out what 8 degrees Celsius means in Fahrenheit? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. Temperature conversion can sometimes feel like solving a math puzzle, but trust me, it’s easier than it seems. Whether you're traveling, cooking, or just curious about the weather, understanding how to convert temperatures is a handy skill to have. In this article, we’ll break it down step by step so you can master it in no time.
Let’s face it, the world isn’t exactly unified when it comes to temperature scales. Some countries swear by Celsius, while others are all about Fahrenheit. If you’re from the US, you’re probably used to Fahrenheit, but if you’ve ever visited Europe or checked global weather updates, you might have stumbled upon Celsius. Knowing how to convert between the two is like having a secret superpower for global communication.
Now, let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of 8 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit. This article will cover everything you need to know, from the basic formula to real-world examples. By the end of it, you’ll be able to impress your friends with your newfound knowledge of temperature conversion. So, buckle up and let’s get started!
Read also:Claire Hill Wine The Quintessential Blend Of Passion And Excellence
Why Does Temperature Conversion Matter?
Imagine this: you’re planning a trip to Paris, and the forecast says it’s going to be 8 degrees Celsius. Do you pack a coat or a t-shirt? If you’re used to Fahrenheit, that number might not mean much to you. This is where temperature conversion comes in handy. Understanding how to switch between Celsius and Fahrenheit can help you make better decisions in everyday life.
But it’s not just about travel. Temperature conversion is also important in fields like cooking, science, and even healthcare. For example, if you’re following a recipe from a European cookbook, you might need to convert oven temperatures from Celsius to Fahrenheit. Or, if you’re monitoring someone’s body temperature, knowing the difference between the two scales can be crucial.
So, why does 8 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit matter? It’s all about being prepared and informed. Whether you’re dealing with weather forecasts, cooking recipes, or scientific data, having a solid grasp of temperature conversion can save you a lot of trouble.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
What is Celsius?
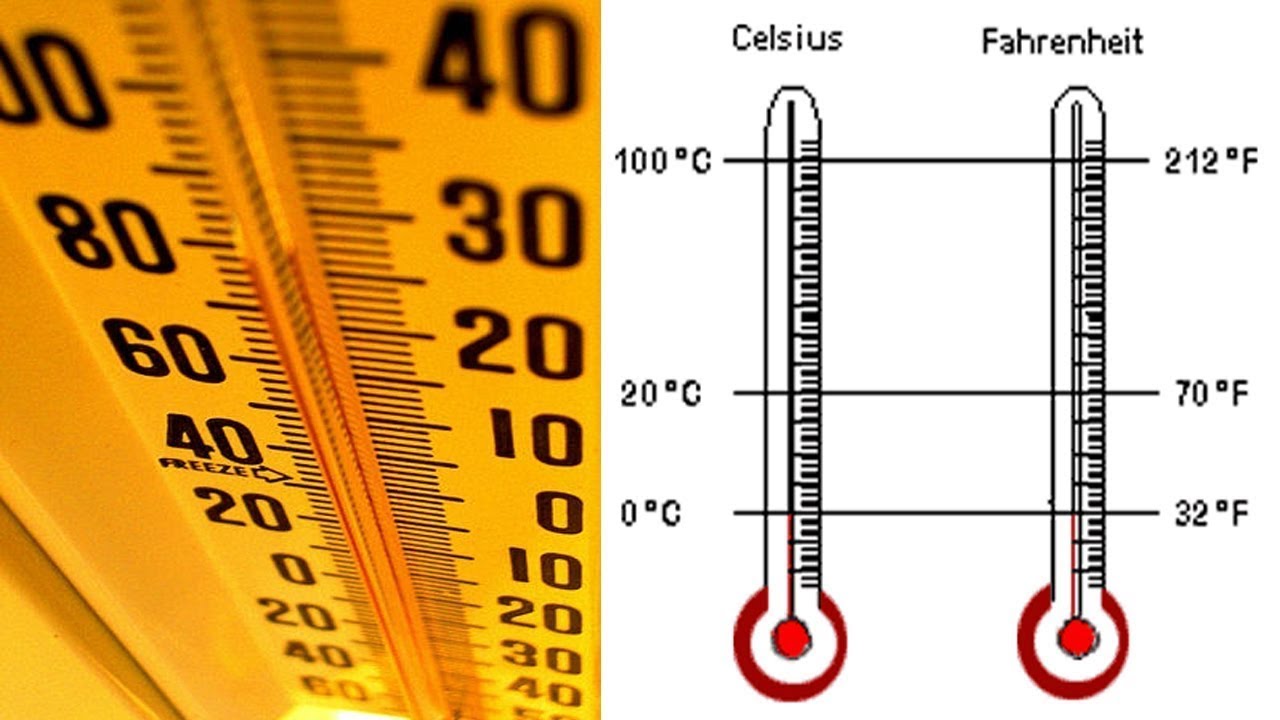
Celsius, also known as centigrade, is the temperature scale used by most countries around the world. It’s based on the freezing and boiling points of water, with 0 degrees Celsius being the freezing point and 100 degrees Celsius being the boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure. This makes it a pretty straightforward system to understand.
For example, if you’re checking the weather in London and it says 8 degrees Celsius, you know it’s going to be chilly but not freezing. Celsius is widely used in scientific research and everyday life in many parts of the world.
What is Fahrenheit?
Fahrenheit, on the other hand, is the temperature scale used primarily in the United States. It was developed by physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. On this scale, the freezing point of water is 32 degrees Fahrenheit, and the boiling point is 212 degrees Fahrenheit at standard atmospheric pressure.
Read also:Fine Line Tattoo Walk In Near Me Your Ultimate Guide To Finding The Perfect Tattoo Spot
So, when you hear that it’s 46 degrees Fahrenheit outside, you might think it’s a bit cool, but not as cold as 8 degrees Celsius. The Fahrenheit scale can feel a bit more complex at first, but with practice, it becomes second nature.
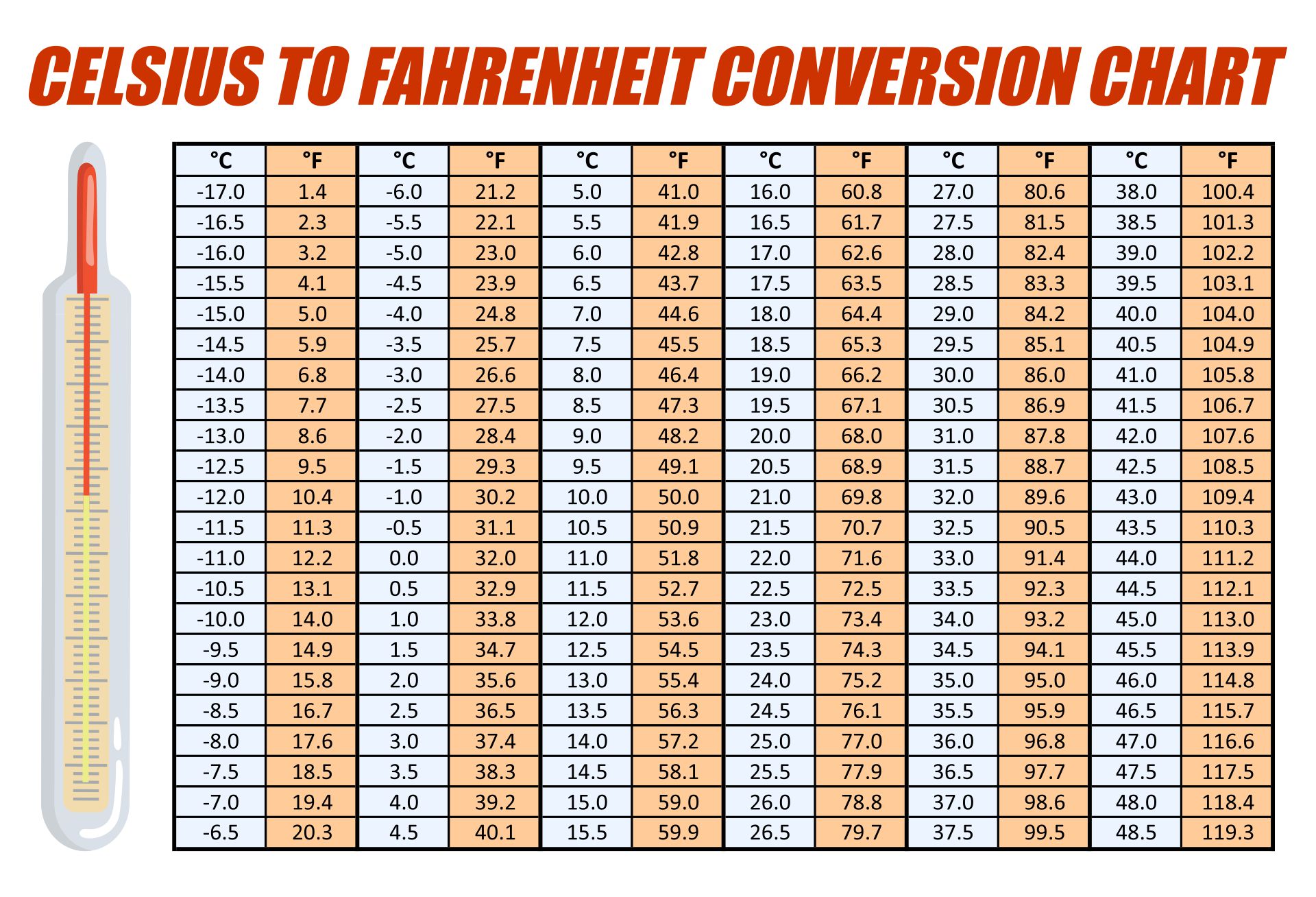
How to Convert 8 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
Now, let’s get to the heart of the matter: how do you convert 8 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit? The formula is simple, and once you’ve got it down, you’ll be converting temperatures like a pro.
Here’s the formula: F = (C × 9/5) + 32. Let’s break it down step by step:
- Start with the Celsius temperature: 8 degrees.
- Multiply it by 9/5 (or 1.8): 8 × 1.8 = 14.4.
- Add 32 to the result: 14.4 + 32 = 46.4.
So, 8 degrees Celsius is approximately 46.4 degrees Fahrenheit. Easy, right? Now you can confidently tell your friends that a chilly 8 degrees Celsius feels like a brisk 46.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
Real-World Examples of Temperature Conversion
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasts are one of the most common places where temperature conversion comes into play. If you’re used to Fahrenheit and you see a forecast for 8 degrees Celsius, you might wonder if you need to bundle up. Knowing that it’s around 46.4 degrees Fahrenheit can help you decide whether to grab a jacket or a sweater.
Cooking and Baking
Cooking is another area where temperature conversion can be super useful. If you’re following a recipe that calls for an oven temperature of 180 degrees Celsius, but your oven only displays Fahrenheit, you’ll need to convert it. Using the formula, you’ll find that 180 degrees Celsius is approximately 356 degrees Fahrenheit. Now you can cook with confidence!
Health and Wellness
Temperature conversion is also important in healthcare. For example, if you’re monitoring someone’s body temperature and the thermometer displays Celsius, but you’re more familiar with Fahrenheit, you’ll need to convert it. A normal body temperature is around 37 degrees Celsius, which is approximately 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit. Knowing this can help you identify potential health issues.
Common Mistakes in Temperature Conversion
While the formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is straightforward, people often make mistakes when doing the math. Here are a few common errors to watch out for:
- Forgetting to multiply by 9/5: Some people skip this step and just add 32 to the Celsius temperature, which gives an incorrect result.
- Rounding too early: It’s important to do the full calculation before rounding the result. For example, 8 degrees Celsius is 46.4 degrees Fahrenheit, not 46 degrees.
- Using the wrong formula: Occasionally, people confuse the Celsius-to-Fahrenheit formula with the Fahrenheit-to-Celsius formula, leading to incorrect conversions.
By being aware of these common mistakes, you can avoid them and ensure your conversions are accurate every time.
Tools and Resources for Temperature Conversion
Online Conversion Tools
If you’re not in the mood for doing math, there are plenty of online tools that can help you convert temperatures quickly and easily. Websites like Weather.com and converters on Google can handle the calculations for you. Just type “8 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit” into the search bar, and voilà! You’ll get the answer in seconds.
Mobile Apps
For on-the-go conversions, mobile apps are a great option. There are plenty of apps available that can convert temperatures, currencies, and more. Some even allow you to input values using voice commands, making them super convenient.
History of Temperature Scales
The Origins of Celsius
The Celsius scale was invented by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742. Initially, he defined 0 degrees as the boiling point of water and 100 degrees as the freezing point, but this was later reversed to the system we use today. Celsius’s scale quickly gained popularity in the scientific community and eventually became the standard for most of the world.
The Origins of Fahrenheit
Fahrenheit was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724. He based his scale on the freezing point of a saltwater solution, which he set at 0 degrees, and the average human body temperature, which he set at 96 degrees. Over time, the scale was refined, and the freezing and boiling points of water were established as 32 and 212 degrees, respectively.
Why Is 8 Degrees Celsius Important?
While 8 degrees Celsius might seem like just another number, it has significance in various contexts. For example, it’s often considered the threshold for “chilly” weather in many parts of the world. If the temperature drops below 8 degrees Celsius, people tend to start wearing heavier clothing and turning up the heat indoors.
In agriculture, 8 degrees Celsius can also be an important benchmark. Some crops are sensitive to cold temperatures, and knowing when the temperature is likely to dip below 8 degrees can help farmers protect their plants.
Tips for Mastering Temperature Conversion
Practice Makes Perfect
The more you practice converting temperatures, the better you’ll get at it. Start with simple numbers like 0, 10, and 20 degrees Celsius, and work your way up to more complex values. Over time, you’ll be able to do the calculations in your head without even thinking about it.
Use Mnemonics
Mnemonics can be a helpful tool for remembering the formula. For example, you could think of “C to F” as “Celsius times 9/5 plus 32.” Creating a memorable phrase can make the process easier and more enjoyable.
Conclusion
Converting 8 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit might seem like a small task, but it’s part of a larger skill set that can be incredibly useful in everyday life. Whether you’re traveling, cooking, or monitoring someone’s health, understanding temperature conversion can make a big difference. By using the formula, practicing regularly, and leveraging tools and resources, you can become a pro in no time.
So, the next time someone asks you what 8 degrees Celsius is in Fahrenheit, you can confidently say it’s 46.4 degrees. And who knows? You might even impress them with your newfound knowledge. Now, go out there and start converting!
Call to Action: If you found this article helpful, feel free to leave a comment or share it with your friends. And if you have any other questions about temperature conversion, don’t hesitate to ask. Happy converting!
Table of Contents
- Why Does Temperature Conversion Matter?
- Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
- How to Convert 8 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Real-World Examples of Temperature Conversion
- Common Mistakes in Temperature Conversion
- Tools and Resources for Temperature Conversion
- History of Temperature Scales
- Why Is 8 Degrees Celsius Important?
- Tips for Mastering Temperature Conversion
- Conclusion