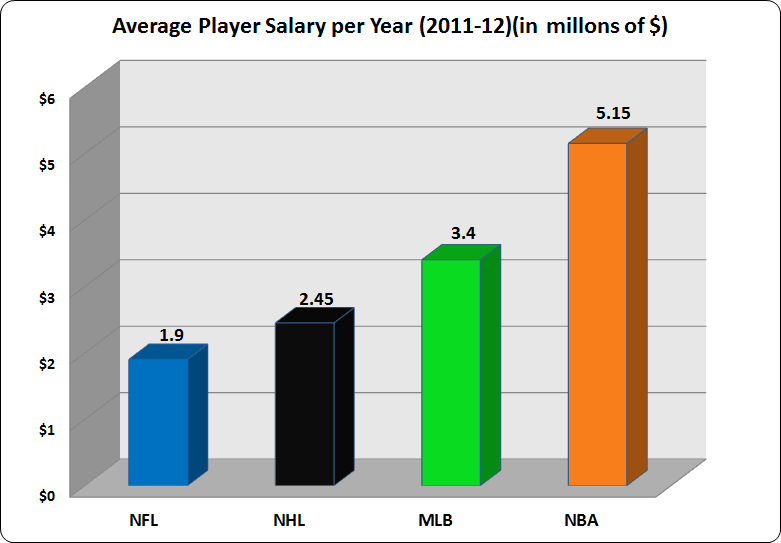
NHL Player Salaries: Average Earnings & Top Earning Players
The compensation of professional ice hockey players in the National Hockey League (NHL) is a significant aspect of the league's structure and player market. This figure is frequently analyzed to understand the financial realities and expectations within the sport. Understanding the prevailing salary represents a benchmark for player performance, contract negotiation, and the overall financial health of the league.
Several factors influence this financial metric, including player position, performance history, and market value. The average salary provides a concise snapshot of the league's pay structure, indicating the general financial resources allocated to players. The historical trends of this compensation reflect the league's evolution and economic shifts. For example, increases over time can signal a growing professional environment for players, while fluctuations can reveal challenges or adjustments in the economic climate affecting the sport. This data is vital to both players considering their futures and team ownership in making informed decisions regarding personnel and resources.
This information is foundational to a broader discussion about player contracts, team finances, and the overall economics of the NHL. Understanding the average salary provides crucial context for further exploration of topics such as player trade values, free agency trends, and the structure of the NHL salary cap.
Average Salary NHL Player
Understanding the average salary of NHL players offers valuable insight into the financial landscape of professional hockey. This data provides context for player compensation, team budgets, and the overall health of the league.
- Compensation
- Performance
- Position value
- Market trends
- Contract negotiation
- League structure
- Salary cap impact
- Economic factors
The average salary reflects a complex interplay of factors. High-performing players command higher salaries, reflecting their impact on game outcomes. Positional value influences compensation; star goalies and top-line forwards often earn more than players in less impactful roles. Fluctuations in market trends, like overall economic conditions, and the NHL's salary cap, directly influence salary levels. Contract negotiation dynamics also shape player compensation. The league's structure, including the draft system and free agency rules, further influences pay scales. These economic factors, combined with a player's value to the team, determine salary negotiation outcomes and the average salary.
1. Compensation
Compensation, in the context of NHL players, directly correlates with the average salary. Understanding the intricacies of this relationship is crucial to grasping the dynamics within the league. The compensation structure, encompassing various factors, shapes the overall financial landscape for players and teams.
- Performance and Positional Value
Player performance, measured by statistics like points, assists, and goals, significantly influences compensation. Elite performers, particularly in high-impact positions like center forwards or top-tier defensemen, command higher salaries. Furthermore, positions requiring specific skills or unique contributions, such as goaltending, also correlate with higher compensation expectations. This demonstrates the link between player output and market value, and a direct relationship to the league's average salary.
- Contract Negotiation and Market Forces
Negotiations between players and teams often hinge on market forces and perceived player value. Strong players with proven track records can leverage their market worth to negotiate higher salaries. Competition among teams, coupled with a player's demonstrable on-ice performance, typically results in a salary reflecting this demand. The interplay between supply and demand within the hockey market strongly influences the average salary.
- Salary Cap and Team Budgets
The NHL salary cap plays a crucial role in the compensation landscape. This limitation on team spending directly impacts the potential salary pool available to teams. Teams with strong financial situations might allocate more to high-profile players, influencing the average salary. This suggests a correlation between cap constraints and the overall compensation framework within the league.
- Historical Trends and Economic Factors
Historical trends in player salaries reveal the impact of economic conditions and league financial health. Economic downturns or periods of high inflation can affect player compensation. The league's revenue stream and overall economic climate influence the potential compensation available to players, hence influencing the average salary.
In conclusion, the components of compensation performance, contract negotiation, team budgets, and economic factors all contribute to the average salary of an NHL player. Understanding these interlinked elements is critical to interpreting the intricacies of player compensation within the NHL's economic framework.
2. Performance
Player performance is a primary determinant of an NHL player's salary. A direct correlation exists between on-ice effectiveness and compensation. This relationship influences team strategies, player expectations, and the overall economic structure of the league. High-performing players command higher salaries, reflecting their market value and the team's investment in maintaining high-level play. This section explores the multifaceted connection between performance and compensation.
- Statistical Metrics
Various statistical metrics directly impact player compensation. Goals, assists, points, plus-minus ratings, and game-winning goals are commonly used to assess a player's contribution to a team's success. Players consistently achieving high numbers in these categories tend to earn higher salaries, reflecting their consistent positive impact on the game's outcome. High-performing goalies, often evaluated based on save percentage and goals-against average, also command significant compensation due to their pivotal role in team success.
- Positional Impact
The position a player occupies also influences performance-based compensation. Players in high-impact positions like center forwards and top-line defensemen frequently have a greater influence on game outcomes than players in secondary roles. This positional influence directly correlates with compensation expectations. The impact of a top-line forward's scoring ability or a shutdown defenseman's defensive prowess is often more substantial than that of a player in a less pivotal position, impacting the average salary structure.
- Consistency and Longevity
Consistent high performance over an extended period significantly impacts a player's salary. Players maintaining a high level of play throughout their careers are valued more highly by teams. Teams are willing to pay a premium for players whose performance remains consistent and impactful over the long haul. This reflects the team's investment in long-term success and the premium placed on sustained performance levels.
- Impact on Team Success
A player's overall impact on team success plays a considerable role. Players whose contributions directly translate into wins or playoff appearances are usually rewarded with higher compensation. This correlation underscores the connection between individual performance, team dynamics, and salary expectations. High-impact players contribute to overall team objectives and can drive a team towards a championship, increasing their value and earning potential.
Ultimately, performance is a complex but crucial factor in determining the average salary of an NHL player. Teams invest financially in players who demonstrate consistent, high-level play, impacting their own success and the league's average compensation structure. The interplay between individual performance, positional value, and team success are inseparable threads in shaping the economic dynamics of the NHL.
3. Position Value
Positional value directly influences the average salary of NHL players. This is a fundamental component of the salary structure, reflecting the varying importance and skill demands associated with different roles on the ice. Players occupying positions requiring specialized skills, high-impact contributions, and greater market demand tend to earn more. The disparity in salary often correlates with the positional responsibility, the frequency of a player's impact on game outcomes, and the perceived value to a team's success.
For instance, goaltenders, pivotal to a team's defensive strategy and performance, often command higher salaries than players in less crucial positions. This reflects the crucial role goaltenders play in securing victories. Similarly, elite center forwards, frequently responsible for generating offense and controlling play, are highly valued and generally earn significantly more than players in less crucial forward positions. Teams recognize the substantial value these players offer to the overall team success. Defensemen who excel in crucial offensive situations or dominate their defensive zone are also compensated accordingly due to their broader impact. The positional value of these skilled players results in higher salaries compared to players in less impactful positions. Conversely, players in less impactful roles, like some depth forwards or specific defensive positions, often earn salaries reflecting their relative contribution to the team.
Understanding the correlation between position and salary is critical for players, teams, and league observers. Teams must consider the positional value when constructing rosters, assessing trade value, and evaluating budgets. Players understand the potential salary range expected based on their respective positions. The public and analysts use this correlation to assess the health of the league's economic structure and player market value. By considering the interplay of these factors, the practical implications become clearer, revealing the multifaceted nature of the average salary within the NHL.
4. Market Trends
Market trends significantly influence the average salary of NHL players. Fluctuations in various economic and competitive forces directly impact the compensation structure within the league. Factors such as overall economic conditions, player demand, and the league's financial health contribute to these trends, impacting player contracts and the overall salary scale.
- Economic Conditions
General economic conditions exert a considerable influence on the average NHL player salary. Periods of economic prosperity often correlate with higher salaries, as teams have greater financial resources to allocate towards player compensation. Conversely, recessions or economic downturns can lead to salary reductions or stagnation. The overall health of the national economy has a direct effect on the financial capacity of NHL teams to pay players, thus affecting the average salary.
- Player Supply and Demand
The balance between available players and team demand also shapes salary trends. A surplus of skilled players in the market might depress average salaries, while a shortage can drive them upward. Factors like the NHL draft, free agency, and player performance influence the supply and demand dynamics. The relative abundance or scarcity of top talent directly impacts the market value and subsequently, the average salary for NHL players.
- League Financial Health
The NHL's financial health directly impacts the average salary of players. Revenue streams from broadcasting deals, merchandise sales, and ticket sales influence team budgets. Strong financial performance by the league generally leads to greater resources for player compensation. Conversely, periods of financial struggle for the league may result in cost-cutting measures, potentially impacting the average salary. This suggests a strong connection between the league's financial prosperity and player compensation.
- Competition Among Teams
Competition among NHL teams for top players shapes the market. High demand for specific players can increase their value, driving up salaries. The competitive landscape within the NHL, including the pursuit of Stanley Cup success, influences the bidding wars among teams. This competitive pressure ultimately affects the average salary by creating a competitive environment where teams invest heavily to secure talent.
In summary, market trends encompassing economic conditions, player supply and demand, league financial health, and competition among teams are interconnected factors influencing the average salary of NHL players. Changes in these areas will inevitably reshape the salary structure, impacting the overall economic dynamics within the league.
5. Contract Negotiation
Contract negotiation is a critical component in determining the average salary of NHL players. The process directly impacts the financial compensation a player receives and, consequently, the overall salary structure within the league. Negotiations are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including a player's performance, market value, and team financial capacity. The outcomes of these negotiations collectively contribute to the average salary figure.
Several factors directly influence the outcome of contract negotiations. Player performance, including statistical metrics and impact on team success, significantly affects their perceived market value. Teams assess a player's contributions to determine the financial investment they are willing to make. Similarly, market value, influenced by external factors like free agency and player demand, also plays a pivotal role. Teams and players navigate the intricate dynamics of the free agent market, aiming to secure favorable terms. Conversely, team budgets and financial constraints are also critical. Teams' financial standing often limits the salary offered to players, regardless of their performance or market value. These factors combine to shape a player's contract, influencing their compensation and, consequently, the average salary.
Real-world examples illustrate the interplay between negotiation and salary. High-performing players, with demonstrably significant contributions to their team's success, often secure contracts exceeding the league's average. Conversely, players with less impressive performance records typically receive compensation closer to the league's average or even below it. Fluctuations in the market value of a player's position can also affect the outcome of negotiations. When the demand for a specific skill set is high, players in those positions tend to command higher salaries. Understanding this interplay is crucial for analyzing the average salary structure. Furthermore, the NHL's salary cap further complicates these negotiations, placing strict limitations on team expenditure and impacting the leverage players and teams have during negotiations. This directly influences the available salary range and impacts the final agreement, thereby directly affecting the average player salary.
Understanding the intricacies of contract negotiations is essential for comprehending the dynamics of player compensation and the league's financial structure. The outcomes of these negotiations directly shape the average salary. Further analysis into the specific negotiation strategies, market trends, and regulatory frameworks within the NHL provides a more thorough understanding of this critical aspect of the league's economy.
6. League Structure
The NHL's structure significantly influences the average salary of its players. This framework, encompassing various components, directly affects the economic dynamics of the league and the compensation players receive. Understanding these structural elements is crucial to comprehending the intricacies of player compensation and the overall financial health of the league.
- Salary Cap and Its Enforcement
The salary cap, a crucial element of the league's structure, directly impacts the average salary. This imposed limit on team spending dictates the maximum amount teams can allocate to player salaries. Variations in cap levels over time directly correlate to changes in the average salary. Strict enforcement mechanisms ensure compliance, preventing teams from exceeding the cap, which maintains financial stability and fair competition, while affecting the total amount available for player compensation.
- Draft System and Entry-Level Contracts
The NHL draft system plays a significant role. The structure dictates the selection order of players entering the league, influencing their early-career compensation. The draft is tied to entry-level contracts, which are influenced by the overall draft position. Higher draft picks sometimes result in lower salaries, compared to a player chosen earlier. The draft and ensuing contracts directly influence the average salary for those entering the league, establishing an early baseline for the player's career compensation.
- Collective Bargaining Agreement (CBA)
The CBA is a fundamental structure outlining the rights and responsibilities of players and teams. This agreement determines the framework for salary negotiations, dispute resolution, and player compensation. Specific clauses regarding salary structure, contract durations, and arbitration processes directly influence the average salary players earn. The stipulations within the CBA directly influence the average salary by establishing the parameters and rules of player compensation.
- Free Agency and Trade Rules
The rules surrounding free agency and player trades influence the salary landscape. These mechanisms can elevate or depress the average player salary. Teams often make strategic trades, impacting salaries based on player value in the market. The free agency process, with its rules about unrestricted and restricted free agents, affects the overall average salary by shaping player movement and team financial maneuvers. These elements affect the overall negotiation dynamics and ultimately influence the average salary.
In conclusion, the interconnected nature of these structural elements establishes the parameters for the average salary of NHL players. The salary cap, draft, CBA, and free agency/trade rules all contribute to the overall compensation framework. Understanding these components allows a comprehensive assessment of how the NHL's organizational structure shapes the financial realities of players and teams, defining the economic climate within the league and influencing the average salary. Variations in these structures will lead to consequential changes in the average salary.
7. Salary Cap Impact
The NHL salary cap significantly influences the average salary of NHL players. This cap, a crucial component of the league's financial structure, directly limits the total amount teams can spend on player salaries. Its impact is pervasive, affecting player compensation, team strategies, and the overall balance of power within the league.
- Impact on Player Compensation
The salary cap acts as a ceiling on player salaries. Within these constraints, the market value of players directly affects their compensation. High-demand players can command higher salaries, but only within the cap's allowance. This often creates a negotiation dynamic where players' worth is measured against the available cap space. Consequently, the salary cap influences the upper and lower bounds of the overall salary range for the league.
- Team Financial Strategies
Teams must strategically manage their salary expenditure to comply with the cap. This impacts team construction, with teams often prioritizing players likely to have a high return on investment. Teams might acquire players through trades, allowing for necessary roster adjustments while remaining within the cap. This maneuvering, in turn, has a ripple effect on the average salary, as teams prioritize players with demonstrable on-ice contributions.
- Influence on Player Value and Negotiation
The cap creates an environment where player value is frequently measured against the available cap space. The negotiation process becomes highly strategic, with teams and players both taking into account the cap's limitations. This often results in salaries aligning with the perceived value of a player within the framework of the cap's constraints, affecting the overall average player salary.
- Impact on Trade Dynamics
The salary cap significantly influences trade negotiations. Teams must ensure that any trade, including acquiring players or releasing them, remains within the cap's bounds. Players with contracts that exceed the cap's projected impact on the team often become trade targets or are released to free up space, further influencing the dynamics of the average salary and the composition of player rosters.
The salary cap is not merely a financial limitation; it is a significant factor shaping the competitive landscape of the NHL. It influences the way teams construct their rosters, the value players command, and the strategies used to maintain financial stability while competing for success. The resulting impact on average salary reflects the dynamic interplay between player value, team budgets, and the overall structure of the league. Understanding this connection provides valuable insight into the league's financial health and the motivations behind player contracts.
8. Economic Factors
Economic factors exert a profound influence on the average salary of NHL players. Fluctuations in the broader economy directly impact the financial capacity of NHL teams to compensate players. Periods of economic prosperity often lead to higher average salaries, reflecting increased revenue streams and team spending power. Conversely, economic downturns can pressure teams to reduce spending, potentially leading to salary stagnation or even reductions.
Several specific economic forces interact to determine the average salary. Inflation, for example, erodes the purchasing power of salaries over time. If salaries do not keep pace with inflation, the real value of a player's compensation decreases. Similarly, changes in the national or global economy can affect the NHL's revenue streams. Increased broadcasting rights fees or greater attendance at games can enable teams to pay higher salaries. Conversely, decreased revenues, stemming from economic hardship or changing consumer preferences, restrict teams' ability to raise salaries.
Examining historical data provides illustrative examples. Periods of economic growth often correspond with periods of increased average player salaries, showcasing a direct correlation. Conversely, recessions or prolonged economic downturns typically result in slower salary growth or even declines in the average salary. For instance, the economic downturn of 2008-2009 corresponded to a period of restrained salary increases or outright decreases for many players, underscoring the influence of broader economic trends. Understanding this historical context underscores the significant impact economic factors exert on player compensation.
The practical significance of this understanding is substantial. For players, acknowledging the impact of economic factors allows for more informed contract negotiations. Teams can use economic analysis to better forecast compensation levels, enabling more effective budgeting and risk management. Moreover, league officials can utilize this understanding to predict the potential impacts of economic cycles on the player market and adjust league policies accordingly. Comprehensive economic analysis becomes a critical tool for all stakeholders, promoting informed decision-making within the financial framework of the NHL.
In conclusion, economic forces play a critical role in determining the average salary of NHL players. Understanding the interconnectedness between broader economic trends and player compensation is paramount for informed decision-making by players, teams, and league administrators. By recognizing these causal relationships, future fluctuations in average salaries can be better anticipated and potentially mitigated.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Average NHL Player Salary
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the average salary of National Hockey League (NHL) players. The following questions and answers provide context and clarity on this topic.
Question 1: What factors influence the average salary of an NHL player?
Several factors contribute to the average NHL player salary. Player performance, measured by statistics and impact on team success, is a significant determinant. Positional value also affects salary, with high-impact positions like center forwards or goalies typically commanding higher compensation. Market trends, encompassing economic conditions and player supply and demand, play a crucial role. Team financial capacity and the NHL salary cap also impose limitations on player compensation. Finally, contract negotiations between players and teams further shape individual salaries and, consequently, the average.
Question 2: How does player performance impact salary?
High-performing players, consistently demonstrating exceptional skills, on-ice contributions, and impacts on team success, typically command higher salaries. Scoring ability, defensive prowess, and overall impact on game outcomes directly correlate with the perceived market value of a player. Consistently strong performance over an extended period reinforces a player's value and often results in a higher salary.
Question 3: What is the role of position in determining salary?
Positions requiring specialized skills and high-impact contributions, such as goaltending or top-line forward positions, often command higher compensation. These positions typically influence a team's success more frequently than other roles. The demand for players filling these specific roles in the market, combined with their demonstrated value to team performance, affects salary expectations.
Question 4: How does the NHL salary cap affect player compensation?
The salary cap, a crucial component of the league's financial structure, directly limits the total amount teams can spend on salaries. This constraint affects negotiations, as player compensation is often determined within this cap's parameters. High-demand players with demonstrated value, nonetheless, can command higher salaries within the cap's allowances.
Question 5: How do economic factors influence the average NHL player salary?
Fluctuations in the overall economy directly affect the NHL's financial capacity. Periods of economic growth typically correlate with higher average salaries, as teams have greater financial resources. Conversely, economic downturns can pressure teams to limit spending, leading to lower salary increases or stagnation.
Question 6: What is the significance of contract negotiations in determining the average salary?
Contract negotiations between players and teams determine the actual salary a player receives. The outcome of these negotiations, influenced by player performance, market value, and team financial constraints, directly impacts the individual salary and, consequently, the average salary. Negotiations are often complex and strategically driven, aiming for a balance between player expectations and team financial realities.
These FAQs provide a foundational understanding of the complex interplay of factors affecting the average salary of an NHL player. This data is critical for players, teams, and observers to comprehend the multifaceted dynamics within the NHL's economic framework.
Further articles within this series delve deeper into specific aspects of NHL player contracts and team financial strategies.
Tips for Understanding NHL Player Salaries
Analyzing the average salary of NHL players requires understanding the multifaceted factors influencing compensation. This section offers practical insights into key determinants, enabling a more nuanced perspective on the league's economic structure.
Tip 1: Performance Drives Compensation. A player's on-ice performance, measured by statistical metrics like goals, assists, points, and plus/minus, significantly influences salary. Elite performers, consistently producing high-impact results, command higher compensation, reflecting their market value and contributions to team success. Teams invest in players whose performance consistently translates to wins and playoff appearances.
Tip 2: Positional Value Impacts Earnings. Specific positions within the NHL carry varying levels of responsibility and impact on game outcomes. High-demand positions, such as top-line forwards and goalies, often yield higher salaries due to the critical role these players play in driving team performance and winning games.
Tip 3: Market Trends Shape Salary Structures. Economic conditions, player supply and demand, and the league's financial health influence salary trends. Periods of economic prosperity generally correspond to higher average salaries, while recessions may lead to salary stagnation or reductions. Teams must assess the broader economic context to accurately evaluate player value.
Tip 4: Salary Cap Influences Negotiation Dynamics. The NHL salary cap imposes a limit on team spending, impacting player compensation. Teams carefully evaluate players' value within this constrained environment. Players with high market value must negotiate within the salary cap framework, aiming for contracts reflective of their performance and market position.
Tip 5: Contract Negotiation Determines Individual Earnings. The contract negotiation process is crucial. Player performance, positional value, market trends, and team financial constraints all influence the final salary agreement. Players and teams engage in strategic negotiation to balance expectations and financial realities, ensuring a compensation package aligned with perceived value.
Tip 6: League Structure Plays a Key Role. The NHL's structure, including the draft system, free agency rules, the collective bargaining agreement (CBA), and the salary cap, all contribute to the overall salary framework. Understanding these structural elements is key to comprehending the complexities of player compensation and the league's economic climate.
Following these tips allows for a deeper understanding of the interconnected factors influencing NHL player salaries. A comprehensive analysis incorporates performance, position, market forces, contractual agreements, and the broader economic context for a more accurate evaluation.
By acknowledging these interconnected factors, a deeper comprehension of the economic drivers within the NHL becomes evident. This understanding is critical for informed analysis of player values and the league's overall financial health.
Conclusion
The average salary of an NHL player is a complex metric reflecting a multifaceted interplay of factors. Player performance, measured by statistical output and impact on team success, directly correlates with compensation. Positional value, a crucial determinant, impacts salary expectations across different roles within the league. Market trends, encompassing economic conditions and player demand, substantially influence the salary structure. The NHL salary cap, a critical component of the league's financial framework, limits team spending and shapes negotiation strategies. Contract negotiations further refine individual compensation, while league structure, including the collective bargaining agreement, defines the parameters within which these negotiations occur. Economic factors, such as inflation and overall economic health, significantly affect the league's financial capacity and, consequently, average salaries.
The factors outlined above demonstrate the intricacy of the NHL's economic ecosystem and the dynamic interplay between players, teams, and the league itself. Understanding these interconnected elements is essential for analyzing the health of the league, anticipating future trends in player compensation, and appreciating the intricate balance of power and influence inherent in this professional sports landscape. Further investigation into specific aspects of player value, team strategies, and the evolving economics of professional sports within the NHL provides valuable insights into the future trajectory of compensation for players. Understanding these details is paramount for future forecasting of the average salary, given the complex dynamics involved.
Article Recommendations
- Georgias Rule Cast Meet The Stars
- Stunning Pixie Cuts Wavy Hair Inspiration Ideas
- Sylvester Stallones 80s Iconic Action Rocky Returns