Mastering Constant Rate Factor: Your Ultimate Guide To Video Encoding Perfection
Hey there, video enthusiasts! If you've ever dabbled in the world of video encoding, you’ve probably stumbled across the term "constant rate factor" or CRF. It sounds like some tech jargon, but trust me, it’s a game-changer. Whether you’re an amateur YouTuber or a professional video editor, understanding CRF can significantly enhance your video quality while keeping file sizes manageable. So, buckle up because we’re diving deep into this fascinating concept.
Let's be honest, video encoding can feel like rocket science at times. You’ve got all these terms flying around—bitrate, frame rate, codecs, and now CRF. But here’s the thing: CRF is one of the simplest yet most powerful tools in your arsenal. Think of it as the secret sauce that helps you strike the perfect balance between video quality and file size. And who doesn’t want that, right?
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about constant rate factor. From its definition to its practical applications, we’ve got you covered. By the end of this, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to optimize your videos like a pro. So, let’s get started and unravel the mysteries of CRF together!
Read also:5 Star Extensions Unlocking The Ultimate Chrome Experience
Here's a quick overview of what we'll cover in this guide:
- What is Constant Rate Factor?
- CRF vs CBR: Understanding the Difference
- A Brief History of Video Encoding
- Optimal CRF Settings for Different Video Types
- Codec Support for CRF
- Best Tools for Using CRF
- Striking the Perfect Balance: Quality vs. File Size
- Pro Tips for Mastering CRF
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- The Future of CRF in Video Encoding
What is Constant Rate Factor?
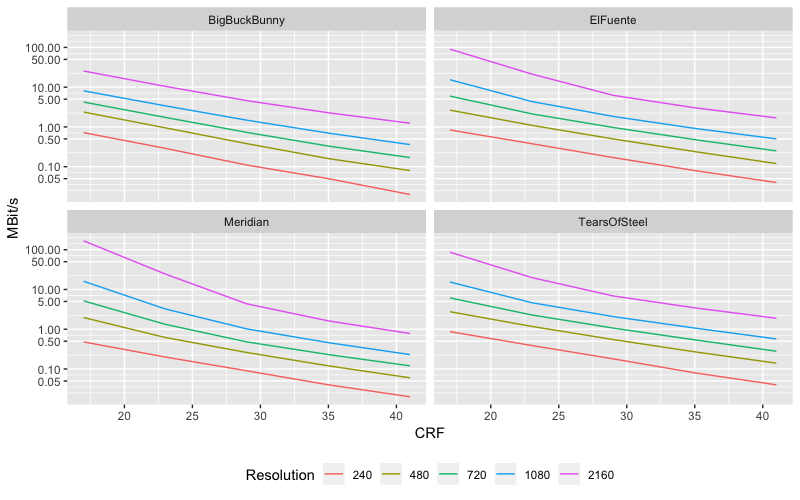
Alright, let’s cut to the chase. Constant Rate Factor, or CRF, is a setting used in video encoding that prioritizes visual quality over file size. Unlike traditional bitrate settings, which control the amount of data used per second, CRF dynamically adjusts the bitrate based on the complexity of each frame. This means that simpler scenes use less data, while complex scenes get the extra attention they need to maintain quality.
Now, here’s the kicker: CRF doesn’t dictate a fixed bitrate. Instead, it uses a scale where lower values result in higher quality (and larger files), while higher values produce smaller files with slightly reduced quality. For most people, a CRF value between 18 and 28 works like a charm, but we’ll dive deeper into that later.
So, why should you care about CRF? Well, it’s all about efficiency. By focusing on quality rather than a rigid bitrate, CRF ensures that your videos look amazing without bloating your storage space. It’s like having your cake and eating it too, but in video encoding form.
How CRF Works Under the Hood
Think of CRF as a smart assistant that analyzes each frame of your video. It assesses how much detail is present and allocates resources accordingly. For instance, a static shot of a serene landscape doesn’t require as much data as a fast-paced action sequence. CRF takes care of this allocation automatically, saving you the headache of manual adjustments.
Here’s a quick breakdown of how CRF works:
Read also:Stretch Lab Holly Springs Your Ultimate Guide To Unlocking Flexibility
- Scene Analysis: The encoder examines each frame to determine its complexity.
- Dynamic Bitrate Allocation: Based on the analysis, the encoder assigns more or less data to each frame.
- Quality Preservation: Even with varying bitrates, CRF ensures that the overall quality remains consistent.
CRF vs CBR: Understanding the Difference
When it comes to video encoding, you’ve got two main approaches: Constant Rate Factor (CRF) and Constant Bitrate (CBR). Both have their pros and cons, but CRF is often the preferred choice for most users. Let’s break down the differences.
Constant Bitrate (CBR): CBR sets a fixed bitrate for the entire video. This means that every frame gets the same amount of data, regardless of its complexity. While this approach is straightforward, it can lead to inefficiencies. Simple scenes might waste data, while complex scenes might suffer from quality loss.
Constant Rate Factor (CRF): As we’ve discussed, CRF is all about flexibility. It adapts the bitrate based on the content of each frame, ensuring optimal quality without unnecessary file bloat. This makes CRF ideal for most modern use cases, especially when storage space is a concern.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | CRF | CBR |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High | Low |
| Quality Consistency | Excellent | Good |
| File Size | Optimized | Fixed |
Why CRF Wins the Battle
In most scenarios, CRF outperforms CBR because it’s smarter and more adaptable. It’s like having a personal assistant who knows exactly how to allocate resources for the best results. Plus, with CRF, you don’t have to worry about manually tweaking bitrates for different parts of your video. The encoder does all the heavy lifting for you.
A Brief History of Video Encoding
Before we dive deeper into CRF, let’s take a quick trip down memory lane. Video encoding has come a long way since the early days of analog recordings. Back in the 80s and 90s, video compression was a luxury reserved for professionals with expensive equipment. Fast forward to today, and anyone with a smartphone can create and share high-quality videos.
The evolution of codecs and compression techniques has been nothing short of revolutionary. From the early days of MPEG-1 to the modern wonders of H.265 (HEVC), each advancement has brought us closer to the perfect balance of quality and efficiency. And at the heart of this evolution lies the concept of CRF, which has become a staple in modern encoding practices.
Key Milestones in Video Encoding
- MPEG-1 (1993): The first major video compression standard, paving the way for digital video.
- H.264 (2003): A game-changer that introduced CRF and became the go-to codec for HD video.
- H.265 (2013): The next generation of video compression, offering even better efficiency and quality.
Optimal CRF Settings for Different Video Types
Now that you understand the basics of CRF, let’s talk about how to use it effectively. Different types of videos require different CRF settings to achieve the best results. Here’s a handy guide to help you get started:
- High-Quality Videos: Use a CRF value between 18 and 22 for stunning visuals with minimal file size.
- Standard-Quality Videos: A CRF value between 23 and 28 is perfect for everyday use, offering a good balance between quality and storage.
- Low-Quality Videos: If you’re tight on space, a CRF value above 28 can significantly reduce file size, though quality will suffer.
Remember, these are just guidelines. The best CRF setting for your video depends on factors like resolution, frame rate, and content complexity. Don’t be afraid to experiment and find what works best for you.
Tips for Finding the Perfect CRF Value
Here are a few tips to help you fine-tune your CRF settings:
- Test Different Values: Encode short clips with various CRF values to see which one meets your quality and size requirements.
- Consider Your Audience: If you’re targeting mobile users, prioritize smaller file sizes. For desktop viewers, focus on higher quality.
- Use Advanced Tools: Many encoding software offer visual quality previews, making it easier to adjust CRF settings on the fly.
Codec Support for CRF
Not all codecs support CRF, so it’s important to choose the right one for your project. The most popular codecs that support CRF include:
- H.264: The industry standard for HD video, widely supported across devices and platforms.
- H.265 (HEVC): The next-generation codec offering better compression and quality than H.264.
- VP9: An open-source codec developed by Google, gaining popularity in web video streaming.
When selecting a codec, consider factors like compatibility, performance, and intended use. For most users, H.264 is a safe bet, but if you’re pushing the limits of quality and efficiency, H.265 or VP9 might be worth exploring.
Why Codec Matters
The codec you choose can greatly impact the effectiveness of CRF. Some codecs are more efficient than others, meaning they can achieve the same quality with less data. This is especially important when working with high-resolution videos, where file sizes can quickly spiral out of control.
Best Tools for Using CRF
Now that you know the theory, let’s talk about the tools. There are plenty of software options available for encoding with CRF, ranging from beginner-friendly to pro-level. Here are some of the best:
- FFmpeg: A powerful command-line tool that offers complete control over encoding settings, including CRF.
- HandBrake: A user-friendly GUI-based encoder that supports CRF and is perfect for beginners.
- Adobe Premiere Pro: A professional video editing software that includes advanced encoding options, including CRF support.
Each tool has its strengths, so choose the one that best fits your workflow and skill level. Whether you’re a command-line wizard or a GUI enthusiast, there’s a tool out there for you.
Getting Started with FFmpeg
For those who prefer the command line, FFmpeg is an excellent choice. Here’s a basic command to get you started:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -c:v libx264 -crf 23 output.mp4
This command encodes your video using the H.264 codec with a CRF value of 23. Adjust the CRF value as needed to achieve your desired quality.
Striking the Perfect Balance: Quality vs. File Size
One of the biggest challenges in video encoding is finding the right balance between quality and file size. CRF makes this process much easier, but it’s still important to understand the trade-offs involved.
Higher CRF values result in smaller file sizes but reduced quality, while lower CRF values produce larger files with better quality. The key is to find a sweet spot that meets your specific needs. For most users, a CRF value between 18 and 23 strikes a good balance.
Practical Tips for Balancing Quality and Size
Here are a few practical tips to help you achieve the perfect balance:
- Start with a High CRF Value: Begin with a value of 23 and gradually decrease it until you’re satisfied with the quality.
- Use Two-Pass Encoding: This method analyzes the entire video before encoding, resulting in better quality and more consistent file sizes.
- Optimize for Your Platform: Different platforms have different requirements. YouTube, for example, recommends specific resolutions and bitrates for optimal playback.
Pro Tips for Master